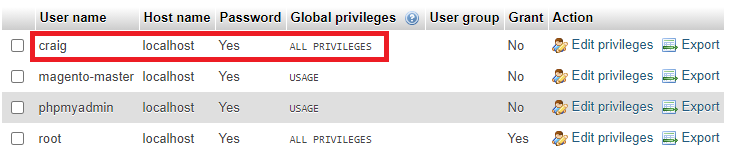
Another way would be to create a MySQL user with all privileges. Basically, a “superuser”.
You create this in the Command Line Interface.
How to create a superuser for MySQL
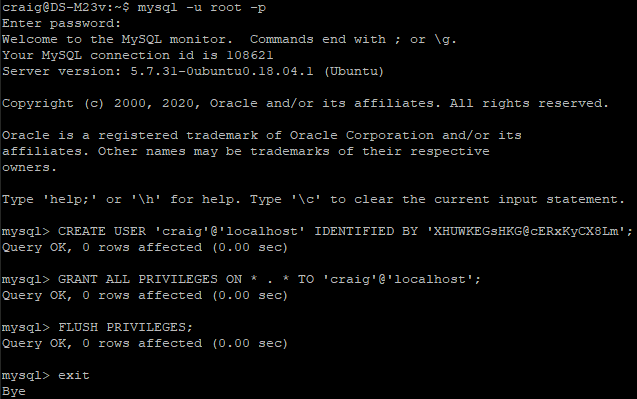
Step 1: After accessing the Command Line Interface, access MySQL (as root) with:
mysql -u root -p
Note: Password prompt requires your MySQL root password (not your OS root password).
Step 2: Create a new user (craig) and set a password (XHUWKEGsHKG@cERxKyCX8Lm):
CREATE USER 'craig'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'XHUWKEGsHKG@cERxKyCX8Lm';
Step 3: Give this new user all privileges:
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON * . * TO 'craig'@'localhost';
Step 4: Flush MySQL privileges for the changes to take affect:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Step 5: Log out of MySQL:
exit
Screenshots
CLI (SSH)
phpMyAdmin